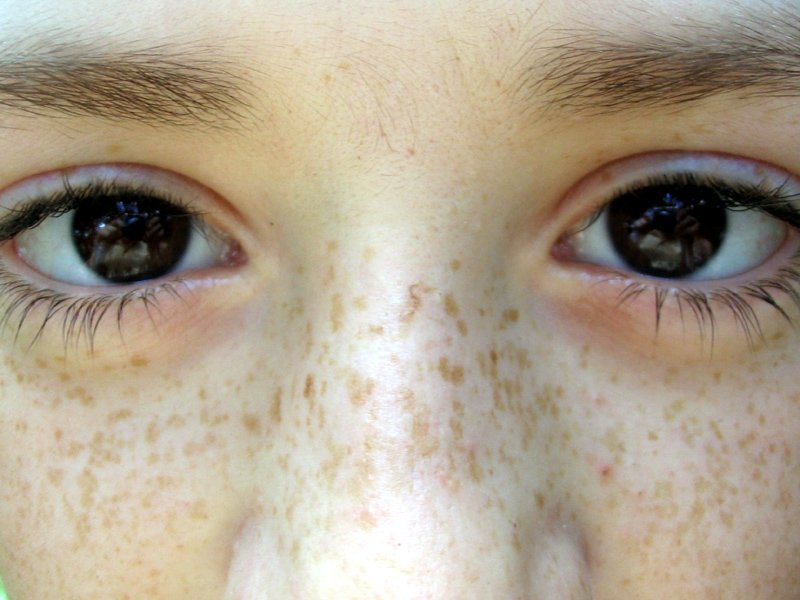
Introduction to Brown Spots
Brown spots, medically known as hyperpigmentation, are a common dermatological concern characterized by patches of skin that appear darker than the surrounding area. This discoloration occurs due to an excess production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Hyperpigmentation can manifest in various forms, including age spots, liver spots, and melasma, each with distinct causes and appearances.
One of the primary causes of brown spots is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. UV rays can accelerate melanin production, leading to sun-induced hyperpigmentation, which often appears on areas frequently exposed to sunlight, such as the face, hands, and shoulders. With aging, the skin’s ability to regenerate diminishes, making it more susceptible to such pigment changes.
Aging itself is another significant factor contributing to the development of brown spots. As the skin matures, cumulative sun exposure and the natural aging process can lead to the formation of age spots, also known as solar lentigines. These spots are typically small, flat, and vary in color from light brown to black.
Hormonal changes, particularly in women, can also lead to hyperpigmentation. Conditions such as pregnancy, oral contraceptive use, and hormone replacement therapy can trigger melasma, a type of hyperpigmentation characterized by larger patches of darkened skin, usually appearing on the face. This condition is often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy” when it occurs in pregnant women.
Individuals with darker skin tones are generally more prone to hyperpigmentation due to the higher baseline levels of melanin in their skin. However, brown spots can affect anyone, regardless of skin type or ethnicity. Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors associated with hyperpigmentation is essential in managing and preventing the appearance of brown spots on the face.
“`
Common Causes of Brown Spots
Brown spots, often referred to as hyperpigmentation, are a common dermatological concern. The primary triggers for these skin changes can vary, but several prevalent causes have been identified. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective prevention and management.
Prolonged Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a significant cause of brown spots. When skin is exposed to UV rays, it produces more melanin as a defense mechanism. Over time, this can lead to the formation of brown patches, especially on areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, and arms. The use of broad-spectrum sunscreen can be an effective preventive measure.
Aging: As we age, our skin undergoes various changes, including a decrease in the turnover rate of skin cells. This can lead to the accumulation of melanin in certain areas, resulting in age spots or liver spots. These are usually benign and more common in individuals over the age of 50.
Genetic Factors: Genetics also play a role in the development of brown spots. Individuals with a family history of hyperpigmentation are more likely to develop similar skin concerns. Genetic predisposition can influence how one’s skin responds to sun exposure and other environmental factors.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly those associated with pregnancy or the use of birth control pills, can lead to a condition known as melasma. Melasma manifests as brown patches on the face and is often exacerbated by sun exposure. Hormonal treatments and sun protection are typically recommended to manage this condition.
Skin Injuries or Inflammation: Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) occurs when an injury or inflammation, such as acne or eczema, heals and leaves a darkened area on the skin. This is due to the overproduction of melanin during the healing process. Proper skin care and treatment of underlying conditions are essential to prevent and reduce PIH.
By recognizing and addressing these common causes, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and prevent the formation of brown spots, thereby maintaining healthier, more even-toned skin.
Types of Brown Spots
Brown spots on the face can appear due to various reasons, and understanding their type is crucial for effective management. The primary categories include sunspots, melasma, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Each type has distinct characteristics and underlying causes, which we will explore to help you identify the specific brown spots you may be dealing with.
Sunspots
Sunspots, also known as solar lentigines or age spots, are flat, brown patches that commonly appear on sun-exposed areas such as the face, hands, and shoulders. They result from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays, which stimulate the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. These spots are typically harmless but can be aesthetically displeasing. Sunspots vary in size and are more prevalent in individuals over 40, although younger people with significant sun exposure can also develop them.
Melasma
Melasma, often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy,” is characterized by larger, symmetric patches of brown or gray-brown discoloration, primarily on the face. It commonly affects the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. Hormonal changes, especially during pregnancy, oral contraceptive use, or hormone replacement therapy, play a significant role in melasma development. Additionally, UV exposure can exacerbate the condition. Unlike sunspots, melasma can be more challenging to treat and often requires a multifaceted approach including sun protection, topical treatments, and sometimes laser therapy.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) occurs following an injury or inflammation of the skin, such as acne, eczema, or even cosmetic procedures. PIH manifests as dark spots or patches where the skin has healed, resulting from an overproduction of melanin during the healing process. Unlike sunspots and melasma, PIH can affect individuals of all skin types and ages. While PIH often fades over time, treatments like chemical peels, topical lightening agents, and laser therapy can expedite the process.
Recognizing the type of brown spots you have is the first step toward effective management. Each type has unique triggers and characteristics, requiring specific treatment approaches for optimal results.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing brown spots on your face is primarily about protecting your skin from excessive sun exposure. A fundamental step in this process is the regular use of sunscreen. Opt for a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to shield your skin from both UVA and UVB rays. Apply it generously on all exposed skin, and remember to reapply every two hours, especially if you’re swimming or sweating. Sunscreen is an essential tool in your arsenal to prevent hyperpigmentation and other sun-induced skin issues.
In addition to sunscreen, wearing protective clothing can significantly reduce the risks of developing brown spots. Wide-brimmed hats, long sleeves, and pants can offer physical barriers against harmful UV rays. Sunglasses with UV protection not only safeguard your eyes but also the delicate skin around them. When possible, seek shade, especially during peak sun hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when the sun’s rays are the most intense.
Beyond sun protection, certain lifestyle changes can also play a crucial role in preventing brown spots. A diet rich in antioxidants helps combat the oxidative stress that can lead to skin damage. Incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables such as berries, spinach, and nuts, which are high in vitamins C and E. These nutrients support skin health and can mitigate the effects of sun exposure.
Hydration is another important factor. Drinking sufficient water keeps your skin hydrated and can improve its ability to repair and renew itself, thus reducing the likelihood of brown spots. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can further protect your skin from premature aging and hyperpigmentation.
Incorporating these prevention strategies into your daily routine can significantly reduce the risk of brown spots and maintain a healthier complexion. Consistency is key, and combining sun protection with a nutritious diet can offer substantial benefits for your skin’s overall appearance and health.
Over-the-counter treatments offer a convenient and accessible option for managing brown spots on the face. Among the most popular products are topical creams containing active ingredients such as hydroquinone, retinoids, and vitamin C. Each of these components plays a significant role in skin lightening and evening out skin tone.
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a widely recognized ingredient in the treatment of hyperpigmentation. It works by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is crucial in the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for brown spots. Typically available in concentrations of 2% for over-the-counter products, hydroquinone can be effective when used consistently over several weeks. However, users should be aware of potential side effects such as skin irritation and redness, and it is advisable to conduct a patch test before full application.
Retinoids
Retinoids, derivatives of vitamin A, are another effective option for treating brown spots. These compounds promote cell turnover and encourage the shedding of pigmented, damaged skin cells. Over-the-counter products may contain retinol, a milder form of retinoid, which can be beneficial for individuals with sensitive skin. It’s important to follow the usage instructions carefully, as retinoids can increase skin sensitivity, particularly to sunlight. Using retinoids in conjunction with a broad-spectrum sunscreen can mitigate this risk.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is renowned for its antioxidant properties and its ability to brighten skin. As an over-the-counter treatment for brown spots, vitamin C works by reducing the formation of melanin and providing protection against UV-induced damage. Products containing vitamin C can be used daily, often in the form of serums, and are generally well-tolerated by most skin types. However, some individuals may experience mild irritation, so starting with a lower concentration and gradually increasing it can be beneficial.
While these over-the-counter treatments can be effective, it is crucial to use them as directed and be patient, as noticeable results may take several weeks to appear. Additionally, consulting with a dermatologist can provide personalized guidance and help in selecting the most appropriate treatment for individual skin concerns.
Professional Treatments
For individuals dealing with stubborn or severe cases of brown spots on their face, professional treatments may offer the most effective solutions. Various dermatological procedures are available, each with unique characteristics, effectiveness, and potential side effects. Understanding these options can help in making an informed decision.
Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin, which causes controlled exfoliation. The depth of the peel can vary from superficial to deep, depending on the severity of the brown spots. Superficial peels often use alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), while deeper peels may use trichloroacetic acid (TCA). Patients can expect some redness and peeling post-procedure, with results typically visible within a few weeks. While effective, deeper peels may require longer recovery periods and carry a higher risk of side effects such as scarring or changes in skin pigmentation.
Laser Therapy: Laser therapy is another advanced option for treating brown spots. It involves targeting the pigment in the spots with concentrated light beams, effectively breaking down the pigment without damaging surrounding tissue. The procedure is generally quick and well-tolerated, with minimal downtime. However, multiple sessions might be necessary for optimal results. Side effects can include temporary redness, swelling, and in rare cases, scarring or changes in skin color.
Microdermabrasion: Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that uses a special device to exfoliate the outer layer of the skin. It helps in reducing the appearance of brown spots by promoting new skin cell growth. The treatment is relatively painless and requires no downtime, making it a popular choice for those seeking a quick solution. However, repeated sessions are often needed to achieve the desired outcome, and temporary redness or sensitivity might occur.
Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves the application of extreme cold to the brown spots, typically using liquid nitrogen. This process freezes and destroys the pigmented cells, leading to the formation of a blister that eventually heals to reveal clearer skin. While cryotherapy is effective, it can cause discomfort during the procedure and may result in side effects such as blistering, scarring, or changes in skin texture.
Ultimately, the choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of the brown spots, skin type, and personal preferences. Consulting with a dermatologist can provide valuable insights into the most suitable and effective options for managing brown spots on the face.
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
For individuals seeking natural solutions to manage brown spots on their face, several home remedies and natural treatments can be effective. One of the most popular ingredients is lemon juice. Known for its natural bleaching properties, lemon juice can help lighten brown spots. To use, simply apply fresh lemon juice directly to the spots with a cotton ball, allowing it to sit for about 15 minutes before rinsing with lukewarm water. It is advisable to perform this treatment twice daily but be cautious as lemon juice can make your skin more sensitive to sunlight.
Aloe vera is another excellent natural remedy. Rich in antioxidants and vitamins, aloe vera promotes skin regeneration and can help fade brown spots. Extract fresh aloe vera gel from the plant and apply it directly to the affected areas. Leave it on for 30 minutes before rinsing with water. Regular use, preferably twice daily, can yield significant improvements.
Apple cider vinegar is also known for its skin-lightening properties. To use, mix equal parts of apple cider vinegar and water, and apply the solution to the brown spots using a cotton ball. Let it sit for a few minutes before rinsing off with water. This treatment can be done once a day. The acetic acid in apple cider vinegar can help reduce pigmentation and improve skin clarity.
Turmeric, a commonly used spice in cooking, contains curcumin which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. To create a turmeric mask, mix one teaspoon of turmeric powder with a few drops of lemon juice and enough milk to form a paste. Apply this mixture to the brown spots, leave it on for 20 minutes, and then rinse off with water. Using this mask two to three times a week can produce noticeable results.
While these natural treatments can be effective, it is important to consider both their pros and cons. Natural remedies are generally safer and have fewer side effects compared to chemical treatments. They are also cost-effective and easily accessible. However, they typically require consistent and prolonged use to see results, and their effectiveness can vary from person to person. Additionally, some natural ingredients may cause allergic reactions or skin sensitivity, so it’s critical to perform a patch test before full application.
When to See a Dermatologist
Monitoring brown spots on your face for any changes is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. While many brown spots are harmless, certain signs indicate that it is important to seek professional help from a dermatologist. One of the primary reasons to consult a dermatologist is if you notice changes in the size, shape, or color of the spots. These changes can sometimes signify underlying skin conditions that require medical attention.
In particular, if a brown spot becomes irregular in shape, increases in diameter, or shifts in color, it is essential to get a professional evaluation. Such transformations might be indicative of conditions such as melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer. A dermatologist can conduct a thorough examination, often using specialized tools like dermatoscopes, to assess the nature of these changes accurately.
Additionally, if brown spots are accompanied by symptoms such as itching, bleeding, or discomfort, this is another strong indicator that you should see a dermatologist. These symptoms can sometimes be associated with more severe skin conditions that necessitate medical intervention. Early detection and treatment of such conditions can significantly improve outcomes and prevent potential complications.
Furthermore, the benefits of getting a professional diagnosis extend beyond identifying serious health issues. A dermatologist can provide you with a tailored treatment plan that addresses your specific skin concerns. This personalized approach can include various treatment options such as topical creams, laser therapy, or other advanced dermatological procedures, ensuring that you receive the most effective care for your skin type and condition.
In summary, while many brown spots are benign, any significant changes in their characteristics or the onset of additional symptoms warrant a consultation with a dermatologist. Professional guidance can provide peace of mind, accurate diagnosis, and a customized treatment plan to manage and potentially eliminate brown spots on your face. Prioritizing professional advice ensures that your skin remains healthy and well-maintained.