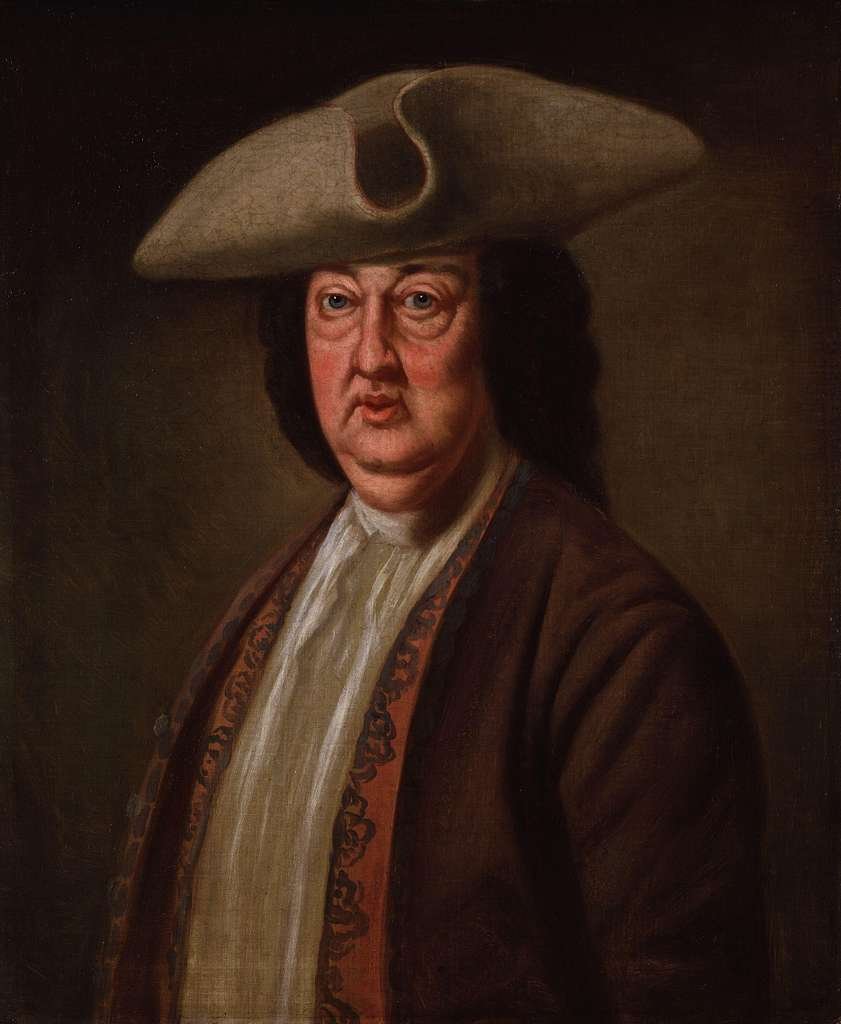
Introduction to Beau Nash
Richard “Beau” Nash, born on October 18, 1674, and passing away on February 3, 1761, was a prominent figure in 18th century England. Renowned for his charisma and style, Nash carved out a significant niche for himself as a celebrated dandy and socialite. His life and influence are particularly notable in the city of Bath, where he played a crucial role in the development of its social and cultural milieu.
Nash’s charm and flair for fashion earned him the affectionate moniker “Beau,” a term synonymous with elegance and sophistication. He became the Master of Ceremonies in Bath, a position that allowed him to reshape the city’s social scene. Under his stewardship, Bath transformed from a provincial spa town into a bustling epicenter of Georgian society, attracting the elite and fashionable from all over England.
Beau Nash’s legacy extends beyond his sartorial choices and social endeavors. He was instrumental in establishing a set of rules and etiquette that governed the behavior of Bath’s visitors. These guidelines not only elevated the city’s reputation but also fostered an environment of decorum and refinement. His influence was such that he is often credited with laying the foundations for what would become the modern concept of the “gentleman.”
Throughout his life, Nash was a figure of both admiration and controversy. His ability to navigate the complexities of high society, coupled with his penchant for gambling and occasional financial troubles, painted a multifaceted portrait of a man who was as complex as he was charming. Despite the challenges he faced, Beau Nash’s impact on Bath and the broader social landscape of 18th century England remains indelible.
As we delve deeper into the life and legacy of Beau Nash, we will uncover the various facets that made him a legendary figure of his time. From his early years to his rise as a social arbiter, Nash’s story is one of ambition, charm, and enduring influence.
Early Life and Background
Beau Nash, born Richard Nash in 1674, hailed from Swansea, Wales. His family was of modest means; his father was a successful mill owner, providing a comfortable yet unremarkable upbringing. From a young age, Nash exhibited a flair for the dramatic and an acute sense of fashion, traits that would later define his legacy as an iconic dandy of the 18th century.
Nash’s early education was undertaken at the prestigious Carmarthen Grammar School, where he demonstrated an aptitude for both academics and social engagements. His eloquence and charm made him a favorite among peers and teachers alike. Recognizing his potential, his parents sent him to Jesus College, Oxford, in hopes that he would pursue a career in law. Although Nash enrolled in the law program, his interest in legal studies paled in comparison to his passion for socializing and fashion.
During his time at Oxford, Nash experienced a significant event that would shape his future. He organized a lavish mock trial, which became the talk of the university. This event showcased his talent for orchestrating grand social occasions and his penchant for the theatrical. It was here that Nash began to cultivate the persona that would eventually make him a celebrated figure in the fashionable circles of England.
After leaving Oxford without a degree, Nash’s early aspirations shifted. He dabbled briefly in the military, serving as an officer, but found the regimented lifestyle unappealing. He soon gravitated towards the bustling social scene of London, seeking to make a name for himself in the capital’s vibrant society. His charm, wit, and impeccable sense of style quickly earned him a reputation among the elite.
These formative years laid the groundwork for Nash’s future endeavors. His upbringing, education, and early experiences cumulatively fostered a unique skill set that he would later leverage to become the Master of Ceremonies at the fashionable city of Bath, a position that cemented his status as a preeminent dandy of his time.
Rise to Prominence in Bath
Beau Nash’s rise to prominence in the city of Bath can be traced back to his appointment as the ‘Master of Ceremonies’ in 1704. This position, though initially informal, allowed Nash to exercise significant influence over the city’s social scene. His primary responsibility was to ensure that the social gatherings and events in Bath were conducted with decorum and elegance. Nash’s keen sense of style and his understanding of social etiquette made him the perfect fit for this role.
One of Nash’s most notable contributions was the introduction of a series of social reforms designed to elevate the city’s status. He implemented strict rules for the conduct of public assemblies, including dress codes and behavior guidelines. These regulations not only maintained order but also enhanced the overall experience for visitors, making Bath a desirable destination for the elite.
Nash’s efforts were instrumental in transforming Bath into a fashionable spa destination. He recognized the potential of Bath’s natural hot springs and worked tirelessly to promote the city’s therapeutic benefits. Under his guidance, Bath’s infrastructure saw significant improvements, including the construction of new buildings and the renovation of existing ones to accommodate the influx of visitors. Nash also organized a variety of entertainment options, such as concerts, balls, and theatrical performances, further solidifying Bath’s reputation as a hub of social activity.
Specific events during Nash’s tenure as Master of Ceremonies highlight his impact. For instance, his introduction of the Beau Nash Assembly Rooms provided a central venue for social gatherings, setting a new standard for sophistication and elegance. Additionally, Nash’s influence extended to the Bath Carnival, an event that drew visitors from across the country, boosting the local economy and enhancing Bath’s prestige.
Through his strategic reforms and charismatic leadership, Beau Nash not only elevated his own status but also cemented Bath’s place as one of the foremost social centers of 18th-century England. His legacy as a dandy and social reformer continues to be remembered and celebrated in Bath to this day.
The Role of ‘Master of Ceremonies’
Beau Nash, an emblematic figure of the 18th-century social scene, held the prestigious title of ‘Master of Ceremonies’ in the bustling city of Bath. This role was not merely ceremonial; it came with significant responsibilities that required both tact and authority. As the ‘Master of Ceremonies,’ Nash was pivotal in shaping the social landscape of Bath, a city renowned for its gatherings of high society.
One of Nash’s primary duties was to establish and enforce rules of social etiquette. In an era where decorum was highly valued, he introduced a set of guidelines that dictated how individuals should conduct themselves in public. These rules were aimed at promoting civility and ensuring that social interactions were conducted with a degree of sophistication. By doing so, Nash fostered an environment where respect and decorum were paramount, enhancing the overall experience of social gatherings.
Nash’s influence extended to the realm of fashion and dress codes. He was instrumental in setting standards for attire, ensuring that guests adhered to a specific dress code that reflected the elegance and refinement of the period. This focus on appearance was not just about aesthetics; it was a reflection of one’s status and respectability. By maintaining strict dress codes, Nash helped to create a visual harmony at events, reinforcing the social hierarchies of the time.
Moreover, Nash’s role involved organizing and overseeing various social events, from balls to public assemblies. His ability to manage these gatherings effectively was a testament to his organizational skills and charisma. He was adept at balancing the needs and egos of the elite, ensuring that events ran smoothly and that disputes were swiftly resolved. Nash’s presence was a stabilizing force, and his reputation for fairness and impartiality earned him the respect of Bath’s high society.
Through his role as ‘Master of Ceremonies,’ Beau Nash left an indelible mark on the social fabric of Bath. His contributions to social etiquette, fashion, and event management not only elevated the city’s status as a cultural hub but also cemented his legacy as a quintessential figure of 18th-century high society.
Beau Nash’s Influence on Fashion and Culture
Beau Nash, a prominent figure in 18th century England, left an indelible mark on both fashion and culture. Known as the ‘Prince of Dandies,’ Nash’s sartorial choices set the standards for high society. His distinctive style, characterized by elaborate attire and meticulous grooming, became a template for the fashionable elite. Nash was instrumental in popularizing trends such as the powdered wig, embroidered waistcoats, and intricate lace details, which were embraced by both men and women of the time.
Nash’s influence extended beyond mere clothing. He was a pioneer in the realm of social etiquette and public behavior. His rules for conduct at the Bath Assembly Rooms, where he served as Master of Ceremonies, transformed these gatherings into sophisticated, orderly affairs. The dress code he enforced at these events dictated a level of elegance and refinement, further cementing his role as a tastemaker. Ladies were expected to wear pastel gowns with corsets and petticoats, while gentlemen donned tailored suits with cravats and silk stockings, epitomizing the era’s opulence.
Beyond fashion, Nash’s impact on culture was significant. He championed the arts, supporting local musicians, playwrights, and painters. His patronage helped Bath become a cultural hub, attracting visitors eager to partake in its vibrant social scene. Under Nash’s influence, Bath evolved into a center for theatrical performances, concerts, and art exhibitions, enriching the cultural landscape of 18th century England.
Moreover, Nash’s contributions to music were notable. He organized regular concerts and promoted the works of contemporary composers, thus ensuring that music became a staple of the social experience in Bath. His efforts in curating a cultivated environment fostered a flourishing artistic community, enabling creativity to thrive.
In summary, Beau Nash’s legacy in fashion and culture is profound. His unique style and stringent social protocols not only defined the aesthetic of his time but also shaped the cultural fabric of 18th century England, leaving a lasting impact that resonated well beyond his era.
Beau Nash, born Richard Nash in 1674, was a British dandy who became an iconic figure in 18th century high society. His personal life was as colorful as the period he lived in, marked by a blend of romantic escapades, friendships, and social connections that defined him as much as his role as the Master of Ceremonies in Bath. Nash’s charm and charisma made him a magnetic presence, drawing the attention of both men and women of prominent social standing.
One of the most notable aspects of Nash’s personal life was his numerous romantic relationships. Although he never married, he was known for his involvement with several women, including the infamous courtesan, Juliana Popjoy. Their relationship was a subject of gossip and intrigue, illustrating Nash’s penchant for the dramatic and the sensational. Despite his numerous liaisons, Nash maintained a certain level of decorum, managing to avoid any long-lasting scandals that could tarnish his reputation.
In addition to his romantic exploits, Nash’s friendships played a significant role in shaping his identity. He was known to be a close confidant of various influential figures, including writers, artists, and politicians. His friendship with the playwright and poet Richard Steele is particularly noteworthy. Steele, a member of the Kit-Cat Club—a renowned 18th-century social club—often spoke highly of Nash, a testament to Nash’s affable nature and social acumen.
Socially, Nash was a master of networking. His ability to cultivate relationships with a wide array of individuals was instrumental in his rise to prominence in Bath. He was perceived by his contemporaries as both a benevolent leader and a skilled mediator, adept at resolving disputes and maintaining harmony within the social scene. His role in organizing social events and setting fashion trends further solidified his status as a central figure in high society.
Notable anecdotes about Nash include his philanthropic efforts. Despite his lavish lifestyle, he was known for his generosity, often using his influence to aid those in need. One such instance was his involvement in the establishment of the Bath General Hospital, a testament to his commitment to social welfare.
Beau Nash’s personal life was a tapestry of relationships, social maneuvering, and a flair for the dramatic. His ability to navigate the complexities of 18th-century society while maintaining his charm and influence speaks volumes about his character and enduring legacy.
Legacy and Impact on Society
Beau Nash, the celebrated Master of Ceremonies at Bath, left an indelible mark on 18th-century society. His influence extended beyond his lifetime, manifesting in various reforms and social innovations that continued to shape Bath and broader English society. Nash’s most significant contribution was his transformation of Bath into a fashionable social hub. His strict enforcement of social etiquette and regulations elevated Bath from a mere spa town to a center of high society, attracting the elite and fostering a culture of refinement and sophistication.
One of Nash’s notable reforms was the introduction of a structured social calendar, which included events like balls, concerts, and assemblies. This organized approach to social gatherings not only enhanced the town’s appeal but also set a precedent for social activities in other parts of England. Nash’s emphasis on proper conduct and dress code helped standardize social norms, influencing the behavior and expectations of the upper classes.
After his death, Nash’s legacy persisted through the continued popularity of Bath as a fashionable destination. The institutions and practices he established endured, ensuring that Bath remained a cultural and social epicenter. His impact is commemorated in various ways, including monuments and literary references. The famous Pump Room in Bath, a central venue for social gatherings during Nash’s time, stands as a testament to his influence. Additionally, Nash’s life and contributions have been immortalized in literature, such as in the works of authors like Georgette Heyer, who drew inspiration from his era.
Historical commemorations further underscore Nash’s enduring legacy. Plaques and statues in Bath honor his contributions, reminding residents and visitors alike of his pivotal role in shaping the city’s history. Through these memorials, Beau Nash’s impact on society is preserved, reflecting his significance as a pioneer of social reform and a key figure in the cultural development of 18th-century England.
“`html
Conclusion: The Enduring Charm of Beau Nash
Beau Nash, a name synonymous with the elegance and sophistication of the 18th century, stands as a testament to the allure of charisma and social acumen. As a master of ceremonies in Bath, his influence extended far beyond mere social gatherings; he was a shaper of cultural norms and a beacon of refined taste. His ability to elevate Bath into a premier social hub is a reflection of his keen understanding of human nature and social dynamics.
Throughout his life, Nash exemplified the characteristics of a true dandy. His impeccable style, witty repartee, and strategic social maneuvering allowed him to navigate and influence the upper echelons of society. He was not just a socialite but a trendsetter who left an indelible mark on the fabric of 18th-century social life. His legacy is evident in the continued fascination with his life and the enduring glamour associated with his name.
The significance of Beau Nash lies not only in his personal achievements but also in what he represents. His story encapsulates the transformative power of charm and wit, the impact of individual agency on broader cultural landscapes, and the timeless appeal of elegance. By examining his life, we gain insights into the dynamics of social influence and the perennial human desire for connection and recognition.
In conclusion, Beau Nash’s enduring charm is a blend of his historical significance and the universal qualities he embodied. His life story continues to captivate us, offering a window into a bygone era while highlighting timeless themes of social interaction and personal influence. As we reflect on his legacy, Beau Nash remains a symbol of the distinguished elegance and the transformative power of a well-cultivated persona.
“`

